Ultimate Guide to Understanding Molded Case Circuit Breakers for Global Procurement
In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical engineering and global procurement, understanding the essential components that ensure safety and efficiency is crucial. Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) are pivotal in this regard, serving as vital protective devices that prevent electrical overloads and short circuits. According to a recent report by Mordor Intelligence, the global MCCB market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2021 to 2026, underscoring the increasing demand for these critical components across various industries. As organizations strive to enhance their electrical systems while ensuring compliance with international standards, having a comprehensive checklist for MCCBs becomes indispensable. This guide aims to demystify MCCB features, specifications, and procurement strategies, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions in a competitive market.

Understanding the Basics: What are Molded Case Circuit Breakers?
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) are essential components in electrical distribution systems, providing protection from overloads and short circuits. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global MCCB market is projected to reach $7.1 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.1%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for electrical safety and reliability in industrial and commercial sectors. MCCBs are designed to automatically disconnect electrical circuits during fault conditions, minimizing the risk of equipment damage and electrical fires.
Fundamentally, MCCBs operate on mechanical and thermal principles, combining both current sensing and thermal overload protection. They are built to handle a specific range of current ratings, typically from 15A to 2500A, making them versatile for various applications. In 2023, research indicates that industries such as mining, oil and gas, and utility sectors are among the largest consumers of MCCBs, reflecting their critical role in maintaining operational safety and efficiency. With advancements in technology, MCCBs are increasingly equipped with smart features that enhance monitoring and control, thereby supporting the trend towards smart grids and energy management systems.
Understanding the Basics of Molded Case Circuit Breakers
This chart illustrates the distribution of molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) based on their current ratings in the global market. It provides an overview of the most common ratings and their corresponding usage percentages.
Key Applications and Industries Utilizing Molded Case Circuit Breakers
 Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) play a crucial role in safeguarding electrical systems across various industries. These devices are engineered to protect against overloads and short circuits, ensuring the reliability and safety of power supply. In sectors like manufacturing, construction, and commercial facilities, MCCBs are predominant due to their versatility and adaptability to different voltage ratings and current capacities. According to a recent market report by Mordor Intelligence, the global molded case circuit breaker market is projected to reach USD 2.25 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2021 to 2026. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on MCCBs for electrical safety in industrial applications.
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) play a crucial role in safeguarding electrical systems across various industries. These devices are engineered to protect against overloads and short circuits, ensuring the reliability and safety of power supply. In sectors like manufacturing, construction, and commercial facilities, MCCBs are predominant due to their versatility and adaptability to different voltage ratings and current capacities. According to a recent market report by Mordor Intelligence, the global molded case circuit breaker market is projected to reach USD 2.25 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2021 to 2026. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on MCCBs for electrical safety in industrial applications.
In addition to manufacturing, the utility sector is another key application area for MCCBs, particularly in the management of electrical distribution systems. These breakers facilitate efficient load management while protecting equipment from potential failures. Furthermore, the rising demand for renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, has led to the increased use of MCCBs in these environments as well, integrating them into systems that require reliable protection for fluctuating loads.
Tip: When selecting an MCCB, consider the specific operational environment and load requirements to ensure optimal performance. Proper installation and regular maintenance enhance the longevity and effectiveness of these devices. Always consult with a professional to tailor the specifications to your unique needs.
Essential Features to Consider in Molded Case Circuit Breaker Selection
When selecting molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) for global procurement, understanding essential features is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Key considerations include the breaker's current rating and short-circuit protection capabilities, as these factors significantly impact the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Additionally, it's vital to assess the thermal-magnetic characteristics of the MCCB, which influence its ability to respond to overload and fault conditions. By focusing on these parameters, procurement professionals can ensure compatibility with their specific operational requirements.
Another important aspect to consider is the design and compatibility of the MCCB within integrated systems, such as DC microgrids. As these systems gain traction in modern energy solutions, ensuring that MCCBs can operate effectively within them is essential. Issues such as voltage ratings and environmental conditions should guide the selection process to enhance system resilience. Furthermore, understanding the differences between MCCBs and other protective devices like miniature circuit breakers can aid in making informed decisions that optimize both performance and cost efficiency.
Ultimate Guide to Understanding Molded Case Circuit Breakers for Global Procurement
| Feature | Description | Importance Level | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Rating | Determines the maximum current the breaker can handle. | High | Ensure it meets the load requirements of your application. |
| Breaking Capacity | The maximum fault current the breaker can interrupt without failure. | High | Select a capacity that exceeds your system's potential fault current. |
| Trip Type | Defines the mechanism by which the circuit breaker trips (thermal, magnetic, etc.). | Medium | Choose based on application requirements and protection characteristics. |
| Frame Size | Size of the breaker that indicates its load handling capability. | Medium | Ensure compatibility with installation space and performance needs. |
| Environment Rating | Indicates the suitability of the breaker for specific environmental conditions. | Medium | Consider temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive materials. |
| Auxiliary Contacts | Additional contacts that can be used for control or indication purposes. | Low | Evaluate needs for signaling and integration into control systems. |
| Standards Compliance | Meeting industry standards for safety and performance. | High | Verify compliance with local and international electrical codes. |
Global Standards and Regulations for Molded Case Circuit Breakers
Molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) are essential components in electrical systems, ensuring safety and reliability by protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits. Understanding the global standards and regulations governing the manufacturing and use of MCCBs is crucial for procurement professionals. Standards such as IEC 60947-2 and UL 489 outline safety requirements, performance criteria, and environmental considerations for these devices. Compliance with these standards not only ensures product reliability but also simplifies the procurement process across different regions.
Furthermore, regional regulations may also impact the selection and application of MCCBs. For instance, in North America, adherence to National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements is mandatory, dictating the specifications and installations of electrical equipment, including MCCBs. In Europe, the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) plays a pivotal role in ensuring that electrical appliances meet safety benchmarks. By staying informed about these regulations, procurement teams can mitigate risks, ensuring that the MCCBs they select not only comply with local laws but also maintain compatibility with global industry standards, facilitating smoother international trade and project execution.
Cost Factors and Budgeting for International Procurement of Breakers
When considering the international procurement of molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs), understanding the cost factors and budgeting is crucial. The global market for MCCBs is projected to grow significantly, with the demand driven by advancements in electrical infrastructure and increased safety regulations. According to a recent report by a leading market research firm, the MCCB market is expected to reach USD 10 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5%. This growth also reflects the rising costs associated with material and manufacturing, which directly impact procurement budgets.

Additionally, budget planning for MCCBs must take into account various cost components beyond just the unit price. Shipping fees, import duties, and local taxes can substantially affect the overall expenditure of international procurement. A detailed cost analysis is vital, as logistics costs can constitute up to 30% of the total procurement budget in some regions. As the competition in the market intensifies, even minor fluctuations in these expenses can become deal breakers for buyers, paralleling challenges in real estate markets where rising prices and low inventory affect buyer decisions. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these cost factors can help organizations navigate the complexities of global procurement effectively.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Manufacturers of Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) in China at the 137th Canton Fair
-

10 Amazing Reasons Why Electronic MCCBs Are Essential for Your Business
-
Top 10 Electronic Circuit Breaker Manufacturers from China at the 137th Canton Fair
-

7 Best Molded Case Circuit Breakers for Optimal Circuit Protection
-

2025 Market Insights: The Future of Best Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers
-

Unmatched Excellence in Manufacturing by Leading Chinese Factory for Best Electrical MCCB Solutions

 JCB1-125
JCB1-125 JCB2-40M
JCB2-40M JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB3-80H
JCB3-80H JCB3-80M
JCB3-80M JCBH-125
JCBH-125 JC125-4P
JC125-4P JCMX
JCMX JCSD
JCSD JCOF
JCOF JCMX1-125
JCMX1-125 JCOF1-125
JCOF1-125 JCSD1-125
JCSD1-125 JCR3HM
JCR3HM JCRD2-125
JCRD2-125 JCRD4-125
JCRD4-125 JCRB2-100
JCRB2-100 JC3RH-2P
JC3RH-2P JC3RH-S
JC3RH-S JC3RH-B
JC3RH-B JC3RH-BS
JC3RH-BS JCR2-63
JCR2-63 JCR1-40
JCR1-40 JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-40M
JCB2LE-40M JCB1LE-125
JCB1LE-125 JCB3LM-80
JCB3LM-80 JCH2-125
JCH2-125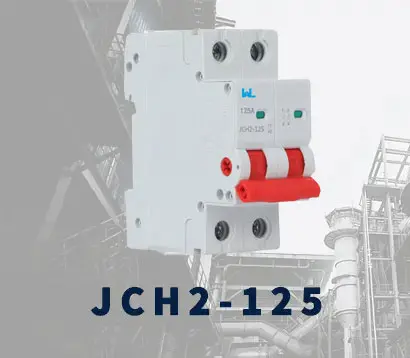 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 CJX2
CJX2 CJ19
CJ19 JCMCU
JCMCU JCHA
JCHA JCSD-40
JCSD-40 JCSD-60
JCSD-60 JCSP-40
JCSP-40 JCSP-60
JCSP-60 JCSPV
JCSPV WEW1-1000
WEW1-1000 WEW1-1600
WEW1-1600 WEW1-2000
WEW1-2000 WEW1-3200
WEW1-3200 WEW1-4000
WEW1-4000 WEW1-6300
WEW1-6300 DC6-125
DC6-125 AX-400-1250
AX-400-1250 AXAL-400-1250A
AXAL-400-1250A AL-400-1250
AL-400-1250 DC3-160
DC3-160 AXS-400-1250A
AXS-400-1250A SHT-125-160
SHT-125-160 UVT-125-160A
UVT-125-160A P-250A-3P-A
P-250A-3P-A 400-3P/4P terminal cover
400-3P/4P terminal cover 1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar
1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar 250-3P terminal conver
250-3P terminal conver WLM6-TCV-160A-3P
WLM6-TCV-160A-3P WLM6-MIP-250A
WLM6-MIP-250A WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-2000A 3P/4P
WLM6-2000A 3P/4P WLM8-125H-3300
WLM8-125H-3300 WLM8-250H-3300
WLM8-250H-3300 WLM8-400H-3300
WLM8-400H-3300 WLM8-400H-4300
WLM8-400H-4300 WLM8-630H-3300
WLM8-630H-3300 WLM8-630H-4300
WLM8-630H-4300 WLM6RT-125A
WLM6RT-125A WLM6RT-160A
WLM6RT-160A WLM6RT-250A
WLM6RT-250A WLM6RT-400A
WLM6RT-400A WLM6RT-630A
WLM6RT-630A WLM6RT-800A
WLM6RT-800A WLM6RT-1250A
WLM6RT-1250A WLM6E-160A-3300 3P
WLM6E-160A-3300 3P WLM6E-250A-3300
WLM6E-250A-3300 WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-630A-3300
WLM6E-630A-3300 WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-1250A-3300
WLM6E-1250A-3300 WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P WLM8E-250H-3300
WLM8E-250H-3300 WLM8E-400H-3300
WLM8E-400H-3300 WLM8E-400H-4300
WLM8E-400H-4300 WLM8E-630H-3300
WLM8E-630H-3300 WLM8E-630H-4300
WLM8E-630H-4300 WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P
WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P WLM6EY-400 3P/4P
WLM6EY-400 3P/4P WLM6EY-630 3P/4P
WLM6EY-630 3P/4P WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P WLM6ELY-160A
WLM6ELY-160A WLM6ELY-250A
WLM6ELY-250A WLM6ELY-400A
WLM6ELY-400A WLM6ELY-800A
WLM6ELY-800A WLM6ELY-1250A
WLM6ELY-1250A WLM8EY-250H-3300
WLM8EY-250H-3300 WLM8EY-400H-3300
WLM8EY-400H-3300 WLM8EY-630H-3300
WLM8EY-630H-3300 WLM6LY-125A
WLM6LY-125A WLM6L-160A
WLM6L-160A WLM6LY-250A
WLM6LY-250A WLM6LY-400A
WLM6LY-400A WLM6LY-800A
WLM6LY-800A WLM6LY-630A
WLM6LY-630A WLM6LY-1250A
WLM6LY-1250A WLM8LY-125H-3300
WLM8LY-125H-3300 WLM8LY-250H-3300
WLM8LY-250H-3300 WLM8LY-400H-3300
WLM8LY-400H-3300 WLM8LY-630H-3300
WLM8LY-630H-3300 JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB1-125DC
JCB1-125DC WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P
WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A 2300
WLM7DC-400A 2300 WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P
WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P WLM7HU-250-3300 3P
WLM7HU-250-3300 3P WLM7HU-315-3300 3P
WLM7HU-315-3300 3P WLM7HU-400-3300 3P
WLM7HU-400-3300 3P WLM7HU-630-3300 3P
WLM7HU-630-3300 3P WLM7HU-800-3300 3P
WLM7HU-800-3300 3P PV-1500V/250A
PV-1500V/250A WEW3-1600
WEW3-1600 WEW3-2500
WEW3-2500 WEW3-4000
WEW3-4000 WEW3-7500
WEW3-7500



