What is a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker and How Does It Work?
In the realm of electrical safety, the significance of a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker cannot be overstated. This device serves as a crucial component in protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, ensuring the safety of both devices and users. Leading expert in electrical engineering, Dr. Emily Garret, has remarked, "A Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker is not just a safety device; it is a critical line of defense that enables the reliable operation of electrical systems."
The dual-action mechanism of thermal and magnetic protection in these circuit breakers allows for a comprehensive approach to fault management. By utilizing thermal sensing to detect prolonged overload conditions and magnetic sensing for instant short circuit issues, Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers exemplify a perfect blend of technology and practicality. As electrical systems continue to evolve, understanding the workings and advantages of such breakers becomes essential for both professionals and consumers alike.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the functionality of Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers, exploring how they operate and why they are indispensable in safeguarding our electrical infrastructures. Through an analysis of their mechanisms, benefits, and applications, we aim to demystify this vital component of modern electrical engineering.

What is a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker?
A thermal magnetic circuit breaker is a crucial component in electrical systems, designed to safeguard circuits from overloads and short circuits. This device operates on two principles: thermal protection and magnetic protection. The thermal aspect includes a bimetallic strip that responds to heat generated by excessive current flow. When the temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the strip bends, triggering the breaker to open the circuit. This mechanism ensures that appliances and wiring are shielded from prolonged exposure to high currents, preventing potential fire hazards.
In addition to thermal protection, the magnetic feature of the circuit breaker provides instantaneous reaction to short circuits. When a fault occurs, a magnetic coil generates a strong magnetic field that quickly pulls a trip lever, disengaging the circuit almost immediately. This dual-action approach makes thermal magnetic circuit breakers highly effective in maintaining electrical safety, as they can handle both gradual increases in current and sudden surges. As a result, they are commonly used in residential and industrial applications, offering reliable protection for both users and equipment.
Key Components of Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers
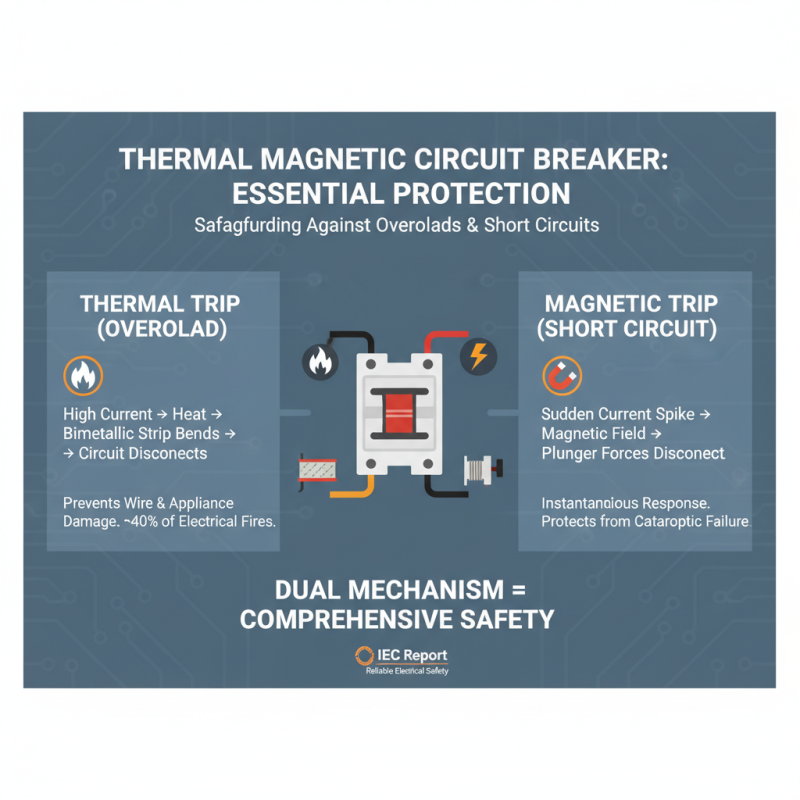
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers are essential protection devices designed to prevent electrical overloads and short circuits. They integrate two key components: thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms. The thermal trip operates on the principle of heat. When excessive current flows through the circuit, it heats a bimetallic strip that bends at a specific temperature threshold, ultimately disconnecting the circuit. This feature is crucial for preventing damage to electrical appliances and wiring due to prolonged overload conditions. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, nearly 40% of electrical fires can be attributed to overloaded circuits, making the thermal aspect vital for safety.
The magnetic trip mechanism, on the other hand, reacts to sudden surges of current, such as those caused by short circuits. It employs an electromagnet that generates a magnetic field proportional to the current flowing through the device. If the current exceeds a predetermined level, the magnet activates the mechanism that trips the circuit, cutting off power almost instantaneously. This rapid response is crucial in minimizing damage and potential hazards. The National Fire Protection Association states that circuit breakers significantly reduce the risk of electrical fires, showcasing their importance in residential and commercial wiring systems.
Tips: Regularly inspect your thermal magnetic circuit breakers for any signs of wear or malfunction. Ensure that they are appropriately rated for your specific electrical load to enhance their effectiveness and longevity. Additionally, consider employing routine maintenance checks by a qualified electrician to ensure optimal performance and safety of your electrical systems.
Operational Principles: Thermal and Magnetic Mechanisms Explained
A thermal magnetic circuit breaker is a crucial component in electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. Its operation is based on two primary mechanisms: thermal and magnetic. The thermal mechanism relies on a bimetallic strip that deforms when excessive current flows through it. As the current increases, the heat generated causes the strip to bend, eventually triggering the breaker to open and interrupt the circuit. This mechanism is effective for protecting against prolonged overload conditions.
On the other hand, the magnetic mechanism reacts to sudden increases in current, such as those occurring during short circuits. This mechanism uses an electromagnet that generates a magnetic field proportional to the current flowing through the circuit. When the current exceeds a predetermined level, the electromagnetic force becomes strong enough to pull a latch that opens the circuit breaker immediately. This quick response is essential for preventing damage to electrical devices and reducing the risk of fire associated with electrical faults. Together, these two mechanisms ensure that thermal magnetic circuit breakers provide reliable protection for electrical circuits by addressing both slow overloads and rapid short circuit conditions.
What is a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker and How Does It Work? - Operational Principles: Thermal and Magnetic Mechanisms Explained
| Component | Function | Mechanism Type | Response Time | Typical Ratings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Element | Detects overload conditions | Thermal Mechanism | 1-2 seconds | 5A - 80A |
| Magnetic Element | Detects short circuits | Magnetic Mechanism | Instantaneous | 10A - 125A |
| Trip Unit | Controls both thermal and magnetic operations | Combined Mechanism | Variable | 15A - 200A |
| Reset Mechanism | Allows for manual reset of the breaker | Mechanical | N/A | Applicable to all ratings |
| Arc Extinguisher | Extinguishes arc during operation | Physical | N/A | Standard across various current ratings |
Industry Standards: Ratings and Performance Benchmarks
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers (TMCBs) are crucial components in electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. These breakers combine thermal and magnetic protection mechanisms, where the thermal element responds to prolonged overloads, and the magnetic component reacts to short-circuit currents. Industry standards play a vital role in evaluating the effectiveness and reliability of TMCBs, defining their ratings, testing methods, and performance benchmarks.
According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), TMCBs are rated based on their ability to handle different current levels and fault conditions. Common ratings range from 15A to 600A, and the devices must meet stringent performance criteria to ensure they trip accurately under defined overload conditions. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) also establishes standards such as IEC 60947-2, which outlines the necessary performance tests and classifications for circuit breakers. These standards guarantee that TMCBs can operate effectively in various environments and are reliable in protecting both people and equipment from electrical hazards.
Performance benchmarks, including tripping times and current interruption ratings, are critical to assess the reliability of TMCBs. For instance, a high-quality TMCB typically exhibits a maximum tripping time of 30 seconds for overload conditions at 6 to 10 times its rated current, while short-circuit interruption ratings may reach up to 65kA, depending on the applications. Such data underscores the importance of selecting TMCBs that not only comply with industry standards but also meet specific operational demands within an electrical system.
Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker Performance Ratings
This chart illustrates the tripping time performance of thermal magnetic circuit breakers at various ratings, demonstrating how response times improve as the current rating increases.
Applications and Benefits of Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers are widely utilized in various applications due to their dual protection mechanism, which combines thermal and magnetic trip elements. These devices offer significant benefits across different sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Their primary application is to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. In homes, they are commonly installed to safeguard wiring and electrical appliances, reducing the risk of fire hazards caused by overloaded circuits.
The advantages of thermal magnetic circuit breakers extend beyond just protection; they also provide a quick response to electrical faults. The thermal component responds to gradual overloads by heating up and eventually tripping the circuit, while the magnetic component reacts instantaneously to short circuits. This combination ensures that electrical faults are addressed swiftly, minimizing potential damage to equipment and ensuring operational continuity.
Moreover, the ease of resetting these breakers after a trip eliminates the need for replacement, making them a cost-effective solution in the long run. Their versatility allows for customization in various settings, making them suitable for different electrical configurations and load requirements.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Low Voltage Circuit Breaker for Your Electrical System Efficiency
-
Understanding Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers: How They Protect Your Electrical Systems
-

Discover the Future of Power Protection: MCCB Innovations Showcased at the 137th Canton Fair
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right MCCB Adjustable for Your Electrical Needs
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Air Breaker Circuit Breakers: Your Complete Resource
-

Understanding Common Issues Faced with Best MCCB Moulded Case Circuit Breakers

 JCB1-125
JCB1-125 JCB2-40M
JCB2-40M JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB3-80H
JCB3-80H JCB3-80M
JCB3-80M JCBH-125
JCBH-125 JC125-4P
JC125-4P JCMX
JCMX JCSD
JCSD JCOF
JCOF JCMX1-125
JCMX1-125 JCOF1-125
JCOF1-125 JCSD1-125
JCSD1-125 JCR3HM
JCR3HM JCRD2-125
JCRD2-125 JCRD4-125
JCRD4-125 JCRB2-100
JCRB2-100 JC3RH-2P
JC3RH-2P JC3RH-S
JC3RH-S JC3RH-B
JC3RH-B JC3RH-BS
JC3RH-BS JCR2-63
JCR2-63 JCR1-40
JCR1-40 JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-40M
JCB2LE-40M JCB1LE-125
JCB1LE-125 JCB3LM-80
JCB3LM-80 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 CJX2
CJX2 CJ19
CJ19 JCMCU
JCMCU JCHA
JCHA JCSD-40
JCSD-40 JCSD-60
JCSD-60 JCSP-40
JCSP-40 JCSP-60
JCSP-60 JCSPV
JCSPV WEW1-1000
WEW1-1000 WEW1-1600
WEW1-1600 WEW1-2000
WEW1-2000 WEW1-3200
WEW1-3200 WEW1-4000
WEW1-4000 WEW1-6300
WEW1-6300 DC6-125
DC6-125 AX-400-1250
AX-400-1250 AXAL-400-1250A
AXAL-400-1250A AL-400-1250
AL-400-1250 DC3-160
DC3-160 AXS-400-1250A
AXS-400-1250A SHT-125-160
SHT-125-160 UVT-125-160A
UVT-125-160A P-250A-3P-A
P-250A-3P-A 400-3P/4P terminal cover
400-3P/4P terminal cover 1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar
1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar 250-3P terminal conver
250-3P terminal conver WLM6-TCV-160A-3P
WLM6-TCV-160A-3P WLM6-MIP-250A
WLM6-MIP-250A WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-2000A 3P/4P
WLM6-2000A 3P/4P WLM8-125H-3300
WLM8-125H-3300 WLM8-250H-3300
WLM8-250H-3300 WLM8-400H-3300
WLM8-400H-3300 WLM8-400H-4300
WLM8-400H-4300 WLM8-630H-3300
WLM8-630H-3300 WLM8-630H-4300
WLM8-630H-4300 WLM6RT-125A
WLM6RT-125A WLM6RT-160A
WLM6RT-160A WLM6RT-250A
WLM6RT-250A WLM6RT-400A
WLM6RT-400A WLM6RT-630A
WLM6RT-630A WLM6RT-800A
WLM6RT-800A WLM6RT-1250A
WLM6RT-1250A WLM6E-160A-3300 3P
WLM6E-160A-3300 3P WLM6E-250A-3300
WLM6E-250A-3300 WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-630A-3300
WLM6E-630A-3300 WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-1250A-3300
WLM6E-1250A-3300 WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P WLM8E-250H-3300
WLM8E-250H-3300 WLM8E-400H-3300
WLM8E-400H-3300 WLM8E-400H-4300
WLM8E-400H-4300 WLM8E-630H-3300
WLM8E-630H-3300 WLM8E-630H-4300
WLM8E-630H-4300 WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P
WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P WLM6EY-400 3P/4P
WLM6EY-400 3P/4P WLM6EY-630 3P/4P
WLM6EY-630 3P/4P WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P WLM6ELY-160A
WLM6ELY-160A WLM6ELY-250A
WLM6ELY-250A WLM6ELY-400A
WLM6ELY-400A WLM6ELY-800A
WLM6ELY-800A WLM6ELY-1250A
WLM6ELY-1250A WLM8EY-250H-3300
WLM8EY-250H-3300 WLM8EY-400H-3300
WLM8EY-400H-3300 WLM8EY-630H-3300
WLM8EY-630H-3300 WLM6LY-125A
WLM6LY-125A WLM6L-160A
WLM6L-160A WLM6LY-250A
WLM6LY-250A WLM6LY-400A
WLM6LY-400A WLM6LY-800A
WLM6LY-800A WLM6LY-630A
WLM6LY-630A WLM6LY-1250A
WLM6LY-1250A WLM8LY-125H-3300
WLM8LY-125H-3300 WLM8LY-250H-3300
WLM8LY-250H-3300 WLM8LY-400H-3300
WLM8LY-400H-3300 WLM8LY-630H-3300
WLM8LY-630H-3300 JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB1-125DC
JCB1-125DC WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P
WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A 2300
WLM7DC-400A 2300 WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P
WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P WLM7HU-250-3300 3P
WLM7HU-250-3300 3P WLM7HU-315-3300 3P
WLM7HU-315-3300 3P WLM7HU-400-3300 3P
WLM7HU-400-3300 3P WLM7HU-630-3300 3P
WLM7HU-630-3300 3P WLM7HU-800-3300 3P
WLM7HU-800-3300 3P PV-1500V/250A
PV-1500V/250A WEW3-1600
WEW3-1600 WEW3-2500
WEW3-2500 WEW3-4000
WEW3-4000 WEW3-7500
WEW3-7500



