What is an MCCB Breaker and How Does it Work?
An MCCB breaker, or molded case circuit breaker, is crucial in electrical systems. It protects circuits from overloads and short circuits. With its ability to interrupt the current flow, it prevents potential damage. Understanding how an MCCB breaker works is essential for both safety and efficiency in electrical installations.
These devices come in various sizes and specifications. Users often overlook the importance of selecting the right one. The operation of an MCCB breaker relies on thermal and magnetic components. When a fault occurs, these parts react quickly. This response can save equipment and prevent fires.
However, many still struggle with proper installation and maintenance. A faulty MCCB breaker can lead to severe consequences. Regular checks and understanding its features can ensure better performance. It's vital to recognize that even the best devices need attention.
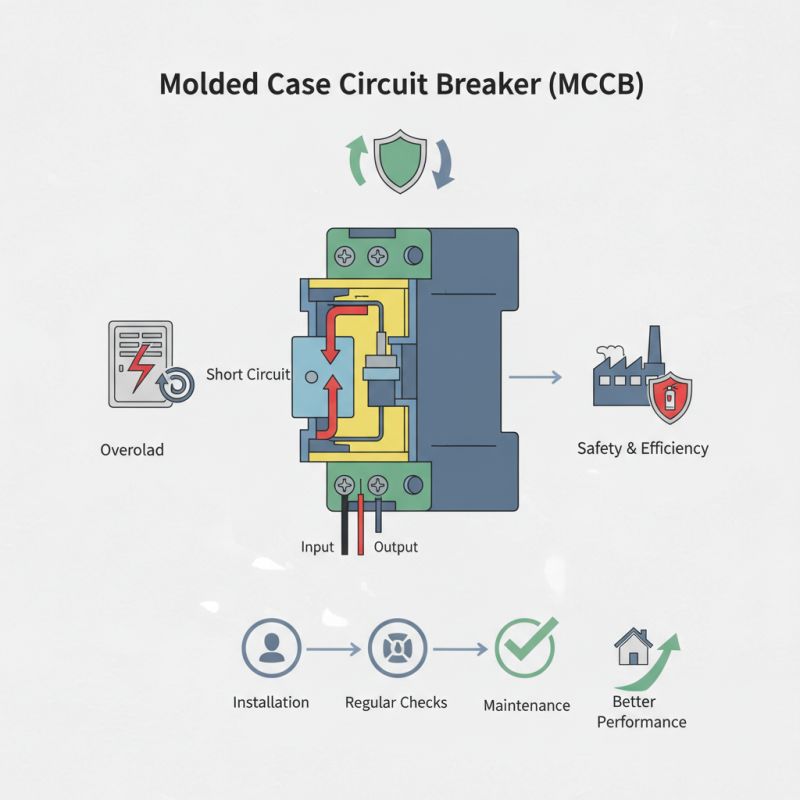
Definition and Purpose of MCCB Breakers
MCCB breakers, or Molded Case Circuit Breakers, play a crucial role in electrical systems. They protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. These devices serve as safety mechanisms that interrupt the flow of electricity. When a fault occurs, the MCCB detects it and switches off the electrical supply. This prevents potential fires and equipment damage.
The primary purpose of MCCB breakers is to ensure safety and reliability in power distribution. They are commonly used in commercial and industrial settings. Their adjustable trip settings provide customization for varying loads. This is important for different applications. However, one might overlook the maintenance of these devices. Neglecting routine checks can lead to failure when needed most. Regular inspections and testing are necessary for optimal performance.
MCCBs come in various ratings and sizes. Choosing the right one requires understanding your specific electrical needs. Over-specifying can lead to unnecessary costs. On the other hand, under-specifying might expose your system to risks. It's essential to evaluate load requirements carefully. Sometimes, the most straightforward choice isn’t the best one. Balancing cost and safety can be challenging.
Key Components of MCCB Breakers
MCCB breakers, or Molded Case Circuit Breakers, play a crucial role in electrical systems. Their key components significantly influence their effectiveness and reliability. The main components include the frame, operating mechanism, and trip unit. Each part serves a unique purpose.
The frame houses the critical components of the MCCB. It's typically constructed from durable materials designed to withstand high temperatures. A recent industry report indicates that over 40% of electrical failures are linked to component degradation. The operating mechanism converts mechanical energy into electrical action. This mechanism is vital for the breaker's operation, yet it can be prone to wear if not maintained properly.
The trip unit is arguably the most essential part. It monitors current and voltage levels, reacting to abnormalities. If excessive current flows, the trip unit intervenes. Studies show that timely intervention by trip units can reduce electrical fires by nearly 30%. However, manufacturers might overlook calibration, leading to malfunction. Regular checks and updates are necessary to ensure the trip unit's reliability. These components, while fundamental, require attention to maintain safety and performance.
What is an MCCB Breaker and How Does it Work? - Key Components of MCCB Breakers
| Component | Function | Material | Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Mechanism | Controls the breaker operation | Plastic and Metal | Actuation force: 1-5 N |
| Poles | Provides connections for phases | Copper or Aluminium | 1, 2, 3 or 4 poles |
| Current Sensing Mechanism | Detects overcurrent conditions | Electromagnetic or Thermal | Rating: up to 630A |
| Trip Unit | Disconnects the circuit under fault conditions | Plastic and Electronics | Adjustable trip settings |
| Auxiliary Contact | Allows remote signaling of the breaker status | Steel | Normally open or closed |
How MCCB Breakers Operate Mechanically
MCCB breakers are crucial in power distribution systems. They protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. Understanding how they operate mechanically is essential for effective use.
These breakers consist of various components. A bimetallic strip bends in response to heat from overload currents. This bending actuates a mechanism, opening the circuit. In short circuits, magnetic coils pull the contacts apart rapidly. The response time is critical in preventing damage to equipment.
Maintaining MCCB breakers is vital. Dust and wear can affect performance. Regular checks help identify issues early. However, not everyone does this regularly. Often, users wait until there's a problem. This reactionary approach can lead to failures. Being proactive is always better when it comes to safety. It’s easy to overlook maintenance, but regular attention is necessary for reliability.
Types of MCCB Breakers and Their Applications
MCCB breakers come in various types, each serving distinct functions. One common type is the thermal magnetic MCCB. This device protects against overloads and short circuits. It uses a thermal sensor to detect excessive heat, while a magnetic element reacts swiftly to fault conditions. Ideal for industrial settings, it balances sensitivity and reliability.
Another variant is the electronic MCCB. It incorporates advanced technology to monitor electrical parameters. This allows for enhanced protection and adjustable settings. Engineers prefer this type for complex setups that require fine-tuning. Its ability to log data makes it useful for ongoing maintenance.
While different types exist, selecting the right MCCB for specific applications can be challenging. The wrong choice may lead to inadequate protection or unnecessary trips. It's crucial to assess the load requirements and environmental conditions. Each type has unique strengths and weaknesses, making thorough evaluation essential.
Types of MCCB Breakers and Their Applications
The following chart illustrates the distribution of various types of MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breakers) and their common applications in different sectors. This data highlights the importance of each type in electrical safety and efficiency.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of MCCB Breakers
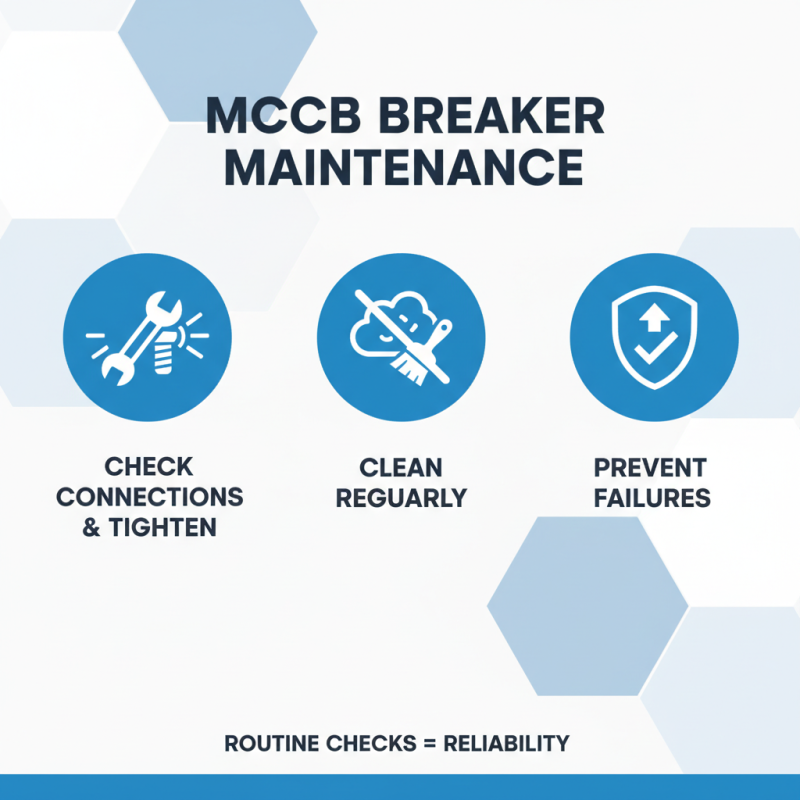
MCCB breakers, or molded case circuit breakers, require regular maintenance to ensure they function correctly. Routine checks can prevent failures. Start by inspecting the connections for any signs of wear. Loose wires can lead to overheating. It's essential to tighten connections when necessary. Dust accumulation can also cause problems, so keep the breaker clean.
If an MCCB trips frequently, it may indicate an underlying issue. This could be due to a short circuit or overload. Testing the tripping mechanism is crucial. Use a multimeter to check for proper function. If the breaker continues to trip without a clear cause, further investigation is needed. Sometimes, consulting with a professional can save time and money.
When troubleshooting, pay attention to the environmental factors. High humidity or extreme temperatures can impact performance. Ensure the unit is installed in a suitable location. Regular visual inspections can identify wear before they lead to failures. Reflect on the maintenance schedule and adjust if necessary. Even minor issues can escalate quickly if overlooked.
Related Posts
-

2025 How to Choose the Right MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) for Your Electrical Needs
-
Top 10 Manufacturers of Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) in China at the 137th Canton Fair
-

Resilient Growth of Chinese-Made Best Electronic MCCBs Amidst US-China Tariff Strife: An Industry Analysis
-

How to Choose the Right MCCB Circuit Breaker for Your Industrial Needs: Key Factors and Data Insights
-

10 Amazing Reasons Why Electronic MCCBs Are Essential for Your Business
-

Why You Should Choose Electronic MCCB for Reliable Circuit Protection

 JCB1-125
JCB1-125 JCB2-40M
JCB2-40M JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB3-80H
JCB3-80H JCB3-80M
JCB3-80M JCBH-125
JCBH-125 JC125-4P
JC125-4P JCMX
JCMX JCSD
JCSD JCOF
JCOF JCMX1-125
JCMX1-125 JCOF1-125
JCOF1-125 JCSD1-125
JCSD1-125 JCR3HM
JCR3HM JCRD2-125
JCRD2-125 JCRD4-125
JCRD4-125 JCRB2-100
JCRB2-100 JC3RH-2P
JC3RH-2P JC3RH-S
JC3RH-S JC3RH-B
JC3RH-B JC3RH-BS
JC3RH-BS JCR2-63
JCR2-63 JCR1-40
JCR1-40 JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-80M
JCB2LE-80M JCB2LE-40M
JCB2LE-40M JCB1LE-125
JCB1LE-125 JCB3LM-80
JCB3LM-80 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 JCH2-125
JCH2-125 CJX2
CJX2 CJ19
CJ19 JCMCU
JCMCU JCHA
JCHA JCSD-40
JCSD-40 JCSD-60
JCSD-60 JCSP-40
JCSP-40 JCSP-60
JCSP-60 JCSPV
JCSPV WEW1-1000
WEW1-1000 WEW1-1600
WEW1-1600 WEW1-2000
WEW1-2000 WEW1-3200
WEW1-3200 WEW1-4000
WEW1-4000 WEW1-6300
WEW1-6300 DC6-125
DC6-125 AX-400-1250
AX-400-1250 AXAL-400-1250A
AXAL-400-1250A AL-400-1250
AL-400-1250 DC3-160
DC3-160 AXS-400-1250A
AXS-400-1250A SHT-125-160
SHT-125-160 UVT-125-160A
UVT-125-160A P-250A-3P-A
P-250A-3P-A 400-3P/4P terminal cover
400-3P/4P terminal cover 1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar
1250-3Pmccb accessories busbar 250-3P terminal conver
250-3P terminal conver WLM6-TCV-160A-3P
WLM6-TCV-160A-3P WLM6-MIP-250A
WLM6-MIP-250A WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-125A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-160A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-630A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1250A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6-1600A-3300 3P/4P WLM6-2000A 3P/4P
WLM6-2000A 3P/4P WLM8-125H-3300
WLM8-125H-3300 WLM8-250H-3300
WLM8-250H-3300 WLM8-400H-3300
WLM8-400H-3300 WLM8-400H-4300
WLM8-400H-4300 WLM8-630H-3300
WLM8-630H-3300 WLM8-630H-4300
WLM8-630H-4300 WLM6RT-125A
WLM6RT-125A WLM6RT-160A
WLM6RT-160A WLM6RT-250A
WLM6RT-250A WLM6RT-400A
WLM6RT-400A WLM6RT-630A
WLM6RT-630A WLM6RT-800A
WLM6RT-800A WLM6RT-1250A
WLM6RT-1250A WLM6E-160A-3300 3P
WLM6E-160A-3300 3P WLM6E-250A-3300
WLM6E-250A-3300 WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-400A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-630A-3300
WLM6E-630A-3300 WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-800A-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-1250A-3300
WLM6E-1250A-3300 WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-1600-3300 3P/4P WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P
WLM6E-2000A-3300 3P/4P WLM8E-250H-3300
WLM8E-250H-3300 WLM8E-400H-3300
WLM8E-400H-3300 WLM8E-400H-4300
WLM8E-400H-4300 WLM8E-630H-3300
WLM8E-630H-3300 WLM8E-630H-4300
WLM8E-630H-4300 WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P
WLM6EY-250-3300 3P/4P WLM6EY-400 3P/4P
WLM6EY-400 3P/4P WLM6EY-630 3P/4P
WLM6EY-630 3P/4P WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-800A 3P/4P WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P
WLM6EY-1250A 3P/4P WLM6ELY-160A
WLM6ELY-160A WLM6ELY-250A
WLM6ELY-250A WLM6ELY-400A
WLM6ELY-400A WLM6ELY-800A
WLM6ELY-800A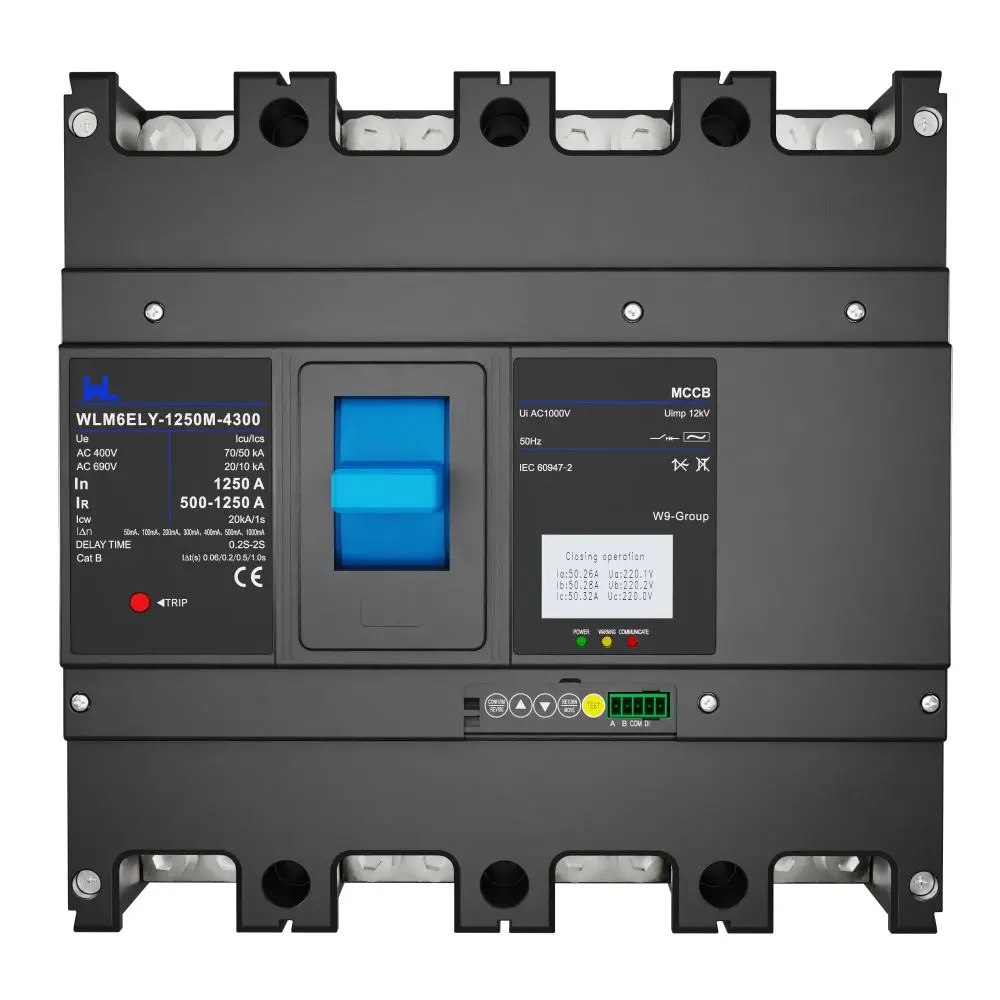 WLM6ELY-1250A
WLM6ELY-1250A WLM8EY-250H-3300
WLM8EY-250H-3300 WLM8EY-400H-3300
WLM8EY-400H-3300 WLM8EY-630H-3300
WLM8EY-630H-3300 WLM6LY-125A
WLM6LY-125A WLM6L-160A
WLM6L-160A WLM6LY-250A
WLM6LY-250A WLM6LY-400A
WLM6LY-400A WLM6LY-800A
WLM6LY-800A WLM6LY-630A
WLM6LY-630A WLM6LY-1250A
WLM6LY-1250A WLM8LY-125H-3300
WLM8LY-125H-3300 WLM8LY-250H-3300
WLM8LY-250H-3300 WLM8LY-400H-3300
WLM8LY-400H-3300 WLM8LY-630H-3300
WLM8LY-630H-3300 JCB3-63DC
JCB3-63DC JCB1-125DC
JCB1-125DC WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-250A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-315A-3300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-400A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P
WLM7DC-630A-3300 3P WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P
WLM7DC-800A-2300 2P/3P WLM7DC-400A 2300
WLM7DC-400A 2300 WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P
WLM7DC-630A-2300 2P WLM7HU-250-3300 3P
WLM7HU-250-3300 3P WLM7HU-315-3300 3P
WLM7HU-315-3300 3P WLM7HU-400-3300 3P
WLM7HU-400-3300 3P WLM7HU-630-3300 3P
WLM7HU-630-3300 3P WLM7HU-800-3300 3P
WLM7HU-800-3300 3P PV-1500V/250A
PV-1500V/250A WEW3-1600
WEW3-1600 WEW3-2500
WEW3-2500 WEW3-4000
WEW3-4000 WEW3-7500
WEW3-7500



